Resilience of a child is something we adults can never stop marveling at, our children are our pride and joy and are the future generation. Giving them the right atmosphere to learn and grow is the best we can do as adults, making the right choice often falls to young and terrified parents who are doing their best. Tough choices are hard to make for ourselves let alone make it for a child who is unaware of the situation and is wholly dependent on you. having said that breathlessness isn’t something to be taken lightly. Imagine being unable to breath or smell anything, scary as it sounds this is the reality of a child suffering from adenoids.
What are adenoids?
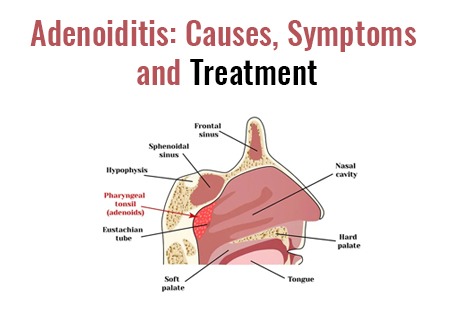
Adenoids are lymphoid tissue that are present at the back of the nasal passage; they are also called palatine tonsils.
What is the purpose of adenoids?
Adenoids are a part of our immune system; they are directly protecting us from any harmful pathogens or foreign bodies we might inhale.
What is adenoiditis?
Increase in the size of the lymphoid tissue at the back of the nose is termed as adenoiditis. Given the location of the adenoid tissue any enlargement will cause immediate symptoms.
Why does it happen?
Although adenoiditis is not hereditary there is a strong correlation between allergy and adenoiditis. Other reasons can be insufficient or improper treatment for rhinitis by ent specialist, dust and pollution have been associated with it.
Symptoms associated with adenoids
- Mouth breathing
- Snoring
- Nasal obstruction
- Runny nose
- Recurrent nasal bleeds
- Frequent ear infections
- Speech difficulty
Diagnosis or tests required
Visit your local ENT Centre adenoids are frequently diagnosed on the basis of patient history, examination of the child and a simple lateral nasal X-ray. Nasal endoscopy is also a very good means for quick diagnosis but children are seldom cooperative.
Treatment
Treatment is again decided on multiple factors, there is medical and surgical management.
Medical management
- Oral decongestants
- Oral anti allergic
- Intra nasal steroids
Surgical management
Endoscopic adenoidectomy is the surgery performed. There are various new instruments used to ensure complete and safe removal of the entire tissue to prevent recurrence.
What happens if left untreated.
- Inability to breath through the mouth will force the child to adopt mouth breathing which inturn can cause repeated throat infections.
- Using the mouth to breath will widen the space between the teeth and the child might develop a nasal twang in voice, speech difficulties and will eventually need braces to give proper teeth alignment.
- The location of the Eustachian tube being close to adenoids the child might develop ear infections, in worse cases the eardrum might rupture leading to hearing difficulties and chronically discharging ears.